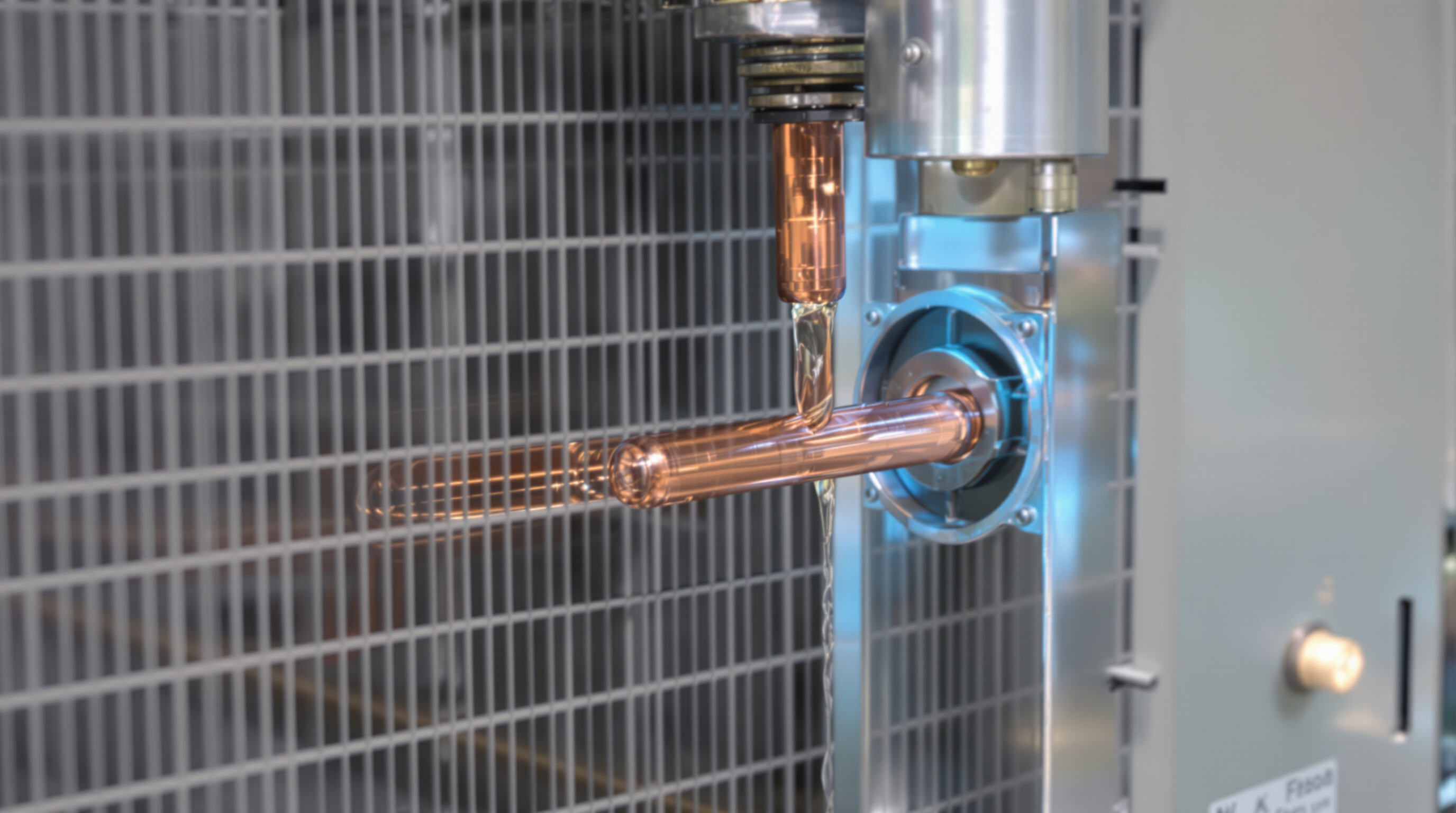

Capillary tubes control how much refrigerant flows through the system because they have such a small inside diameter, usually between half a millimeter and two millimeters. When hot, pressurized refrigerant comes out of the condenser and goes into these tiny tubes, there's lots of friction which drops the pressure by around 85%, according to research from Ponemon in 2023. The sudden drop in pressure makes the refrigerant expand quickly, getting colder in the process until it becomes this chilly mix of liquid and vapor just before hitting the evaporator coil where most of the cooling actually happens.
Capillary tubes are used in about 89 percent of home air conditioning units as fixed-orifice expansion devices, taking the place of those complicated mechanical valves we see elsewhere (according to ASHRAE data from 2023). These little tubes are typically constructed from either copper or stainless steel materials. They help regulate how much refrigerant flows into the evaporator section, which ultimately improves how well the system absorbs heat from indoor air. The reason these components have become so widespread? Simple design combined with dependable performance makes them perfect for large scale manufacturing operations. Especially important for manufacturers targeting budget conscious consumers who need reliable cooling solutions without breaking the bank at AC capillary tube production facilities around the country.
Flow regulation is determined by three primary factors:
Optimized capillary tube design has been shown to improve SEER ratings by 12–15% in inverter AC systems through stable refrigerant flow, according to recent HVAC system design improvements.
Metals that resist corrosion play a critical role when materials need to withstand repeated temperature changes and harsh chemicals over time. Most air conditioning units still rely on copper for their internal components, with around three out of four AC systems using it because copper conducts heat so well and can be shaped easily during manufacturing according to recent HVAC industry data from 2023. For refrigeration systems that handle ammonia specifically, stainless steel becomes the go to material since it stands up better against corrosive effects. Brass alloys find their niche in certain low pressure situations where other materials might not work as effectively, though these applications tend to be quite specialized within the industry.
Seamless copper tubes are produced via cold-drawing processes that achieve 0.5% dimensional tolerance. Inline X-ray gauging monitors wall thickness during drawing, maintaining uniformity within ±0.01 mm—critical for accurate refrigerant metering in precision AC systems.
Electrolytic-tough-pitch (ETP) copper with ≤0.04% oxygen content prevents hydrogen embrittlement during brazing. After annealing, tubes are targeted to reach 65 HRB on the Rockwell B scale, balancing ductility and pressure resistance. Automated vision systems inspect all tubes for compliance with ASME B36.19M diameter tolerances prior to shipment.
AC capillary tube factories use multi-pass cold drawing to achieve diameters as small as 0.5 mm with ±0.01 mm accuracy. Copper stock is reduced over 6–12 stages using tungsten carbide dies, ensuring consistent wall thickness. Real-time laser measurement systems maintain dimensional stability during high-speed production runs exceeding 25 m/min.
Optimized die geometry (12°–16° approach angles) and oxalic acid-soap lubricants reduce drawing friction by 38% compared to petroleum-based alternatives (TheZebra.org 2021). A progressive die sequence maintains drawing ratios between 1.15 and 1.35 per pass, enabling up to 75% total cross-sectional reduction without inducing material defects.
Between drawing stages, copper tubes undergo batch annealing at 450–550°C in nitrogen-controlled furnaces. This restores ductility (≥35% elongation) and ensures complete recrystallization within 90 minutes. Metallographic analysis verifies microstructural integrity before further processing.
CNC flying cutters section tubes into 1.5–6 m lengths with ± 2 mm precision at speeds up to 30 m/min. Servo-driven coiling systems produce spools weighing 150–300 kg, maintaining coil diameter consistency within 0.5 mm. Polymer interleaving layers prevent surface damage during handling and transport.
Surface quality directly impacts refrigerant flow and system reliability. A smooth interior finish (below 0.8 µm Ra) minimizes turbulence and prevents particulate accumulation that could lead to micro-clogging. Surface imperfections exceeding 5% of wall thickness may reduce cooling capacity by 12–18% (HVAC Tech Journal, 2023), underscoring the need for rigorous manufacturing controls.
After drawing, tubes undergo nitric acid pickling to remove oxide layers, followed by a three-stage deionized water rinse to eliminate residual chemicals. High-velocity air knives dry the tubes at 65–80°C, reducing moisture content to below 50 ppm—a critical step in preventing internal corrosion.
Final packaging occurs in ISO Class 5 cleanrooms, with tubes sealed in nitrogen-flushed containers to inhibit oxidation. Automated handling systems minimize human contact, while laser particle counters verify cleanliness per MIL-STD-1246E. Top-tier facilities maintain contamination levels at ≤10 particles/cm² for particles larger than 0.5 µm.
Each tube is tested at 2.5× its operating pressure (typically 500–800 psi) for 10–15 minutes to confirm structural integrity. This hydrostatic test detects microleaks as small as 0.003 mm and ensures reliability under real-world refrigerant pressures, in line with ASHRAE 2024 guidelines.
Laser micrometers and ultrasonic gauges verify outer diameter within ±0.01 mm and wall thickness within ±5%. These measurements ensure consistent flow characteristics and are monitored in real time, with non-conforming units automatically rejected to meet ASTM B280 compliance.
Accelerated life testing simulates 15 years of service through 50,000 pressure cycles (50–300 psi) and thermal shocks from -40°C to 120°C. To qualify for warranty coverage, tubes must retain at least 95% of their initial burst strength (≥1,200 psi) after testing.
Each tube is marked with a laser-etched code enabling full traceability to raw materials, process parameters, and inspection records—supporting 10-year audit requirements.
Capillary tubes are finding their way into more inverter driven heat pumps these days, especially as manufacturers need components that perform reliably under varying pressure conditions beyond what traditional split systems require. The move towards greener alternatives like R-290 refrigerant has pushed many factory owners to rethink their operations. About 42 percent of those making AC capillary tubes have revamped their production processes since early last year. These upgrades focus on preventing issues with hydrogen embrittlement while keeping pace with new safety regulations that continue to evolve in this sector.
Capillary tubes primarily function as fixed-orifice expansion devices, regulating the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator section to enhance heat absorption from indoor air.
Copper is commonly used due to its excellent thermal conductivity and ease of shaping, making it suitable for high-quality air conditioning components.
Pressure drop is controlled by tube geometry, length, and refrigerant properties, which influence flow resistance and pressure differential.
The ASTM B280 standard specifies 99.9% pure copper, ensuring compatibility with modern refrigerants and defining key properties like tensile strength and oxide contamination limits.